The DaVinci Robot was originally devised by NASA and DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) to remotely operate on soldiers on the battlefield, in the absence of surgery equipment and surgeons were not available. However, the project failed due to financial issues. Undaunted and convinced of the huge potential of this technology, MIT engineers bought its patent. The DaVinci Robot has since become the most famous surgeon robot in the world. It is designed to facilitate complex surgery using a minimally invasive approach. A surgeon controls the DaVinci Robot from a console.
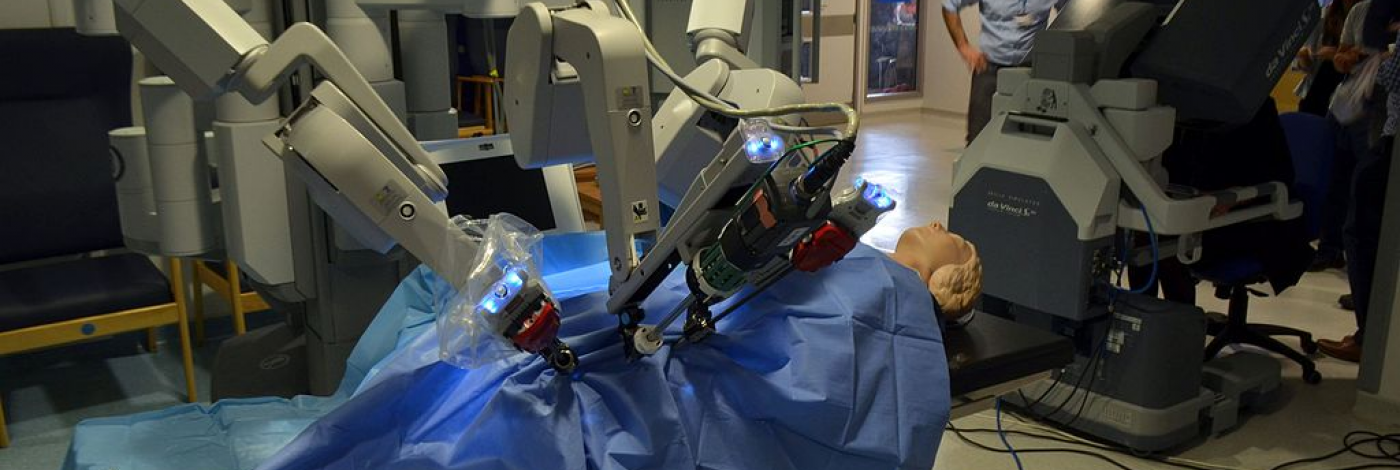
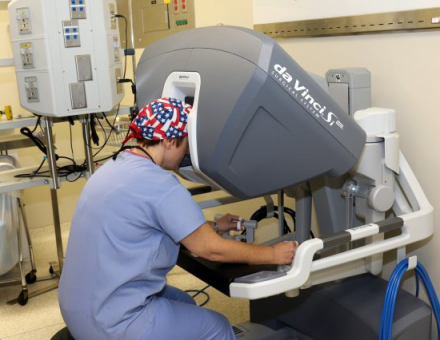
The DaVinci Robot is based on remote human-computer interaction: a surgeon doesn’t have scalpels anymore, but instead he handles levers behind a console, looking on a screen.
In this way, the DaVinci Robot allows remote surgery - surgeons can operate on patients who are hundreds or even thousands of miles away.
The DaVinci Robot is probably the most striking example of the application of telemedicine, which is one of the most important trends in the health industry.
Telemedicine applications
Telemedicine is not a recent practice. For numerous years, emergencies have been regulated by phone (via 911) through which doctors can have a chat with a patient or a witness for medical purposes.
Nevertheless, the practice of telemedicine is on the rise, which is principally due to the increase in quality network and the extensive use of data in health industry.
Telemedicine has many applications :
- Teleexpertise: a doctor or a specialist can ask another doctor for advice and opinion about a patient; It’s perhaps the oldest form of telemedicine
- Teleconsultation: a doctor can conduct a consultation remotely, by phone, chat, or video chat
- Remote monitoring: a patient’s condition can be tracked through automatic and remote systems; it can launch an alert to a specialist if it’s necessary
Teleconsultation: a response to societal change
Teleconsultation responds to societal change. It facilitates communication not only between doctors and patients, but also between doctors. Its advantages include the improvement of access to care and reduction of health costs. The applications of teleconsultation are especially strong for the follow-up of chronic diseases, psychiatric follow-up, and post-operative follow-up in outpatient surgery, among others.
In many countries across the world, doctors can hold consultations through phone or video call. It is highly useful for certain medical conditions or issues such as sore throats, asthma, skin rash, and fever.
Teleconsultation is especially helpful in locations that are remote from major cities and in places that have neither doctors nor hospitals in the surrounding area.
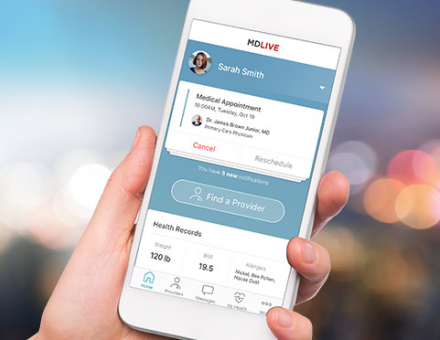
Many startups have tapped into the new market of teleconsultation. For example, in the US, MDLIVE's offers online consultations via online video, phone or mobile app. with licensed physicians in all 50 states for non-emergency issues.
Moreover, MDLIVE provides health plans, health systems, and self-insured employers, delivering large-scale health services.
Similar to physical clinics and hospitals, telemedicine service providers are regulated in most countries across the world. In the US, telemedicine services are conducted through an HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) platform and process.
Remote monitoring: tracking, following up long-term conditions
Remote monitoring has also met with a tremendous development: remotely monitoring diabetes, heart rate, and blood pressure remotely is now possible with reduced operating costs. For example, the new iWatch generation (Apple Watch Series 4) has this capability.
It includes an EKG feature, with back crystal electrodes that reads the electrical heart impulses in the wrist and a digital crown that reads the electrical heart impulses in the fingertip.
The new iWatch allows patients to collect data from his heart health and communicate data to his doctor. It also has a fall detection function, that can detect a fall and automatically call the local emergency services if the holder does not answer within 60 seconds.
The FDA has approved the EKG feature, signifying that the iWatch can be used as a medical device.
Requisite high standard of network quality required
Network performance is certainly the key to the development of telemedicine.
For a teleconsultation, if it’s a not an emergency, a slowdown or an interruption of service is not a main issue in non-emergency situations; however, things are different for a surgery!
In this regard, applications must be lightweight and mobile friendly, and network quality must be beyond reproach. The development of 5G and fiber-optic networks facilitates the expansion of telemedicine.
New approach to the doctor-patient relationship
Telemedicine is increasingly popular among patients, but it still encounters cultural and other obstacles by calling into question certain fundamental aspects of the doctor-patient relationship.
First, telemedicine implies a non-physical relationship between a doctor and a patient, because both parties are separated by screens. Nonetheless, the relationship is not a virtual one because interactions are real and doctors can deliver an accurate diagnosis and spot-on advice.
Secondly, telemedicine goes hand in hand with a patient centric approach, as patients can follow-up, track and access their medical records and information.
Finally, telemedicine is a major aspect of the revolution in the health industry. It is transforming the method of taking care of patients and offering reduced operating costs for health stakeholders.
Do you want to take part in the digital transformation in Health Industry?
The MSc in Health Management & Data Intelligence run by emlyon business school allows you to become a specialist able to navigate in today’s industry impacted by artificial intelligence and digital transformation.


